- Home
- >
- News
- >
- Industry News
- >
- Why does an engine have intake and exhaust?
Why does an engine have intake and exhaust?
Why does an engine have intake and exhaust?
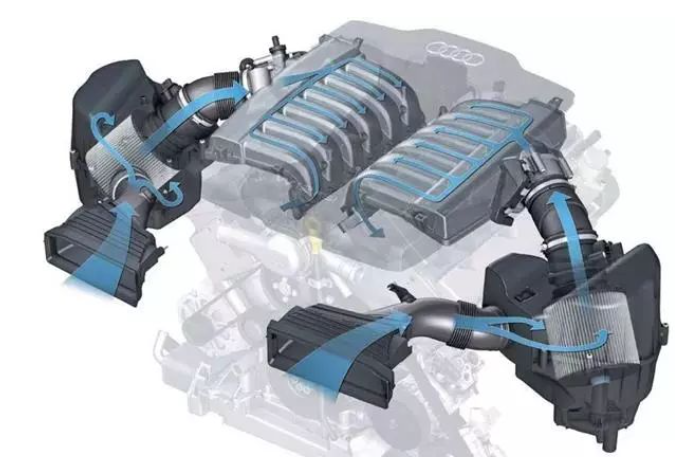
1.The role of the intake system
• Provide oxygen: The essence of combustion is the chemical reaction between fuel and oxygen.
The intake system introduces air (containing oxygen) into the cylinder to ensure that the fuel can be fully burned.
• Mixed fuel: In a gasoline engine, the intake manifold mixes air with atomized fuel to form a combustible mixture (diesel engines directly inject fuel into the cylinder).
• Cooling effect: The intake airflow can help cool the internal components of the engine (such as cylinder walls and pistons).
• Boost optimization: Turbocharged or supercharged engines improve combustion efficiency and power by forcibly increasing the intake volume.
2. The role of the exhaust system
• Exhaust gas: The exhaust gas after combustion (such as CO₂, water vapor, nitrogen oxides, etc.)
needs to be discharged in time to avoid occupying the cylinder space and affecting the next combustion.
• Reduce back pressure: The optimized exhaust design reduces exhaust residue and improves intake efficiency. The diameter and length of the exhaust pipe will affect engine performance.
• Environmental protection and noise reduction: The exhaust system includes a catalytic converter (reducing harmful emissions)
and a muffler (reducing noise) to meet environmental regulations and comfort requirements.
• Turbine drive: In a turbocharged engine, the exhaust gas drives the turbine to rotate, thereby driving the compressor on the intake side to increase the intake pressure.
3. The coordinated work of intake and exhaust The engine completes energy conversion through a four-stroke cycle (intake, compression, power, exhaust) or a two-stroke cycle:
1. Intake stroke: The piston moves downward, the intake valve opens, and fresh air or mixed gas is inhaled.
2. Compression stroke: The valve is closed, and the piston moves upward to compress the mixed gas.
3. Power stroke: The spark plug ignites (or diesel compression ignition), and the mixture burns and pushes the piston downward.
4. Exhaust stroke: The exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves upward to discharge exhaust gas. If there is a lack of intake, combustion cannot start;
if there is a lack of exhaust, the retention of exhaust gas will cause a sharp drop in efficiency or even flameout.
4. Comparison of special cases
• Two-stroke engine: Intake and exhaust are synchronized through piston movement (no independent valves),
but the efficiency is low and the pollution is high, mostly used in small equipment.
• Rotary engine: Intake and exhaust are achieved through the movement of the rotor, the structure is different but the principle is similar.
Summary Intake and exhaust are the core links of the engine's "breathing": intake provides raw materials for combustion, and exhaust removes waste.
The two work together to ensure that the engine runs continuously, efficiently and cleanly. Modern technologies (such as variable valve timing and turbocharging) further optimize this process,
improving performance and environmental protection.