- Home
- >
- News
- >
- Industry News
- >
- Why do turbochargers use intercoolers?
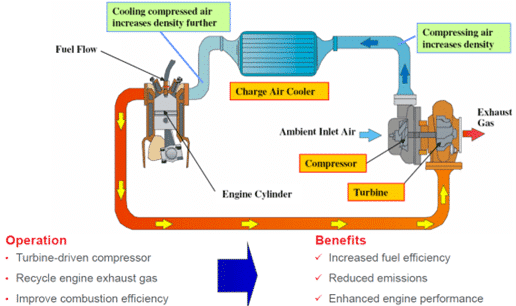
Why do turbochargers use intercoolers?
Why do turbochargers use intercoolers?
1. Reduce the intake temperature and increase the air density
• Thermodynamic principle: When the turbocharger compresses the air, the gas temperature rises significantly (following the ideal gas law 𝑃𝑉=𝑛𝑅𝑇).
High temperature causes the air to expand, the density decreases, and the amount of oxygen actually entering the cylinder decreases.
• Function of the intercooler: By cooling the compressed air (usually reducing it by 50-100°C), the intercooler increases the air density,
allowing more oxygen to participate in combustion, thereby enhancing power output and combustion efficiency.
2. Suppress knock and protect the engine
• High temperature risk: High temperature intake will increase the temperature of the combustion chamber,
increase the risk of knock (premature self-ignition of the mixture), damage the engine and reduce performance.
• Cooling effect: The intercooler reduces the intake temperature, reduces the tendency of knock, allows a higher compression ratio or boost pressure, and optimizes power tuning.
3. Improve combustion efficiency and environmental protection
• Sufficient oxygen: The cooled high-density air ensures more complete combustion of the fuel, reduces the emission of unburned hydrocarbons and particulate matter,
and meets environmental protection standards.
• Balance between power and economy: Efficient combustion can both increase power and reduce fuel consumption (especially reducing "turbo lag" when the turbo is involved).
4. Reduce heat load and extend life
• Heat dissipation requirements: High temperature air increases engine thermal stress and affects the life of components (such as pistons and valves).
Intercoolers indirectly reduce combustion temperature, reduce heat load, and improve reliability.
5. Type and design selection
• Air-cooled intercooler: Simple structure, relying on external airflow, suitable for most civilian vehicles, but limited cooling efficiency under extreme conditions.
• Water-cooled intercooler: Using coolant circulation, compact size and stable cooling, suitable for engines with high boost or limited space (such as high-performance vehicles).
Summary The intercooler is an indispensable component in the turbocharger system.
It improves air density and combustion efficiency through physical cooling, while solving the problems of knock and durability caused by high temperature.
Although it increases system complexity and cost, its advantages in power improvement, fuel economy and engine protection far outweigh the potential disadvantages.