- Home
- >
- News
- >
- Industry News
- >
- What is a twin-scroll turbocharger?
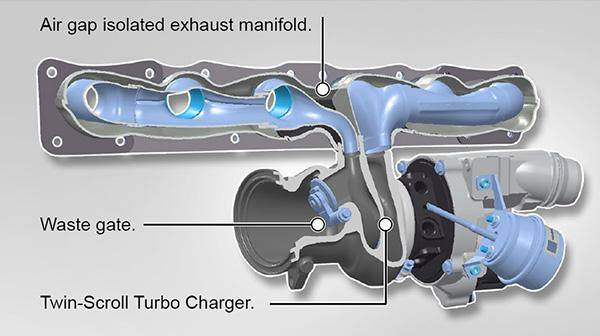
What is a twin-scroll turbocharger?
The twin-scroll single turbocharger is an advanced turbocharging technology designed to optimize engine performance,
especially in reducing turbo lag and improving low-speed response. Here is a detailed analysis:
Working Principle
Twin-scroll design: The exhaust manifold is divided into two independent channels (scrolls),
which usually group the engine's cylinders (such as a four-cylinder engine is divided into 1-3 cylinders and 2-4 cylinders). The exhaust of each group of cylinders is guided to the turbine through its own scroll.
2. Single turbine structure: The two scrolls converge into the same turbine, but through separate inlets to ensure
that the exhaust pulses do not interfere with each other, thereby driving the turbine blades more efficiently.
Core Advantages
• Reduce turbo lag: By separating the exhaust pulses, maintaining continuous exhaust airflow, the turbine responds faster at low speeds.
• Improve low-speed torque: Optimize exhaust energy utilization, enhance the boost effect at low speeds, and improve acceleration performance.
• Simplified structure: Compared with the twin-turbo system, the single-turbo design reduces complexity and cost while reducing weight.
Technical Features
• Exhaust pulse optimization: The exhaust pulses after grouping drive the turbine alternately to avoid mutual cancellation of airflow and improve turbine efficiency.
• Wide application: Commonly used in gasoline engines (such as BMW N55), balancing performance and cost, and partially replacing traditional twin-turbo solutions. Potential Disadvantages
• High speed limit: A single turbine may face exhaust flow restrictions at extremely high speeds, affecting maximum power output.
• Design complexity: The twin-scroll exhaust manifold requires precise design, which may increase manufacturing costs and installation space requirements.
Comparison with other technologies
• Twin turbocharging: Twin turbos (large and small turbines or parallel) cover a wider speed range, but are costly and complex in structure; twin-scroll single turbos achieve similar effects with simplified design.
• Variable geometry turbine (VGT): VGT adapts to different speeds by adjusting the turbine blades, but its high temperature tolerance limits its application in gasoline engines; twin-scrolls improve efficiency through physical separation and are more suitable for gasoline engines. Practical application and effect
• Model example: BMW N55 engine (replacing N54 twin-turbo) adopts this technology to achieve smoother power output and lower maintenance costs.
• Performance improvement: Actual measurements show that low-speed torque is increased by about 10-15%,
turbo response time is shortened, and fuel consumption and emissions are also optimized.